Question: What are the differences between hi-fi and DJ/broadcast phono cartridges?
Answer: When shopping for a new turntable or selecting a new or replacement phono cartridge you may notice some substantial differences between the many models offered today. Differences not only in price, but in the materials used to make them and differences in their form and function. This post will focus on two types of cartridges, each designed with a specific application in mind. One designed with the goal of producing audio of the highest possible fidelity (usually within the confines of a given price point) for casual listening at home (hi-fi use), and the other with the primary goal of withstanding the rigors of heavy use and abuse in a commercial application such as that of a DJ, turntablist or broadcaster. Let’s look at some of the differences between the two so you can determine which is best for your application.
The Stylus
There are three basic stylus shapes, with multiple variations available for some of them. They are, spherical (conical), biradial (elliptical) and hyper-elliptical (line contact, MicroLine, Shibata etc.)
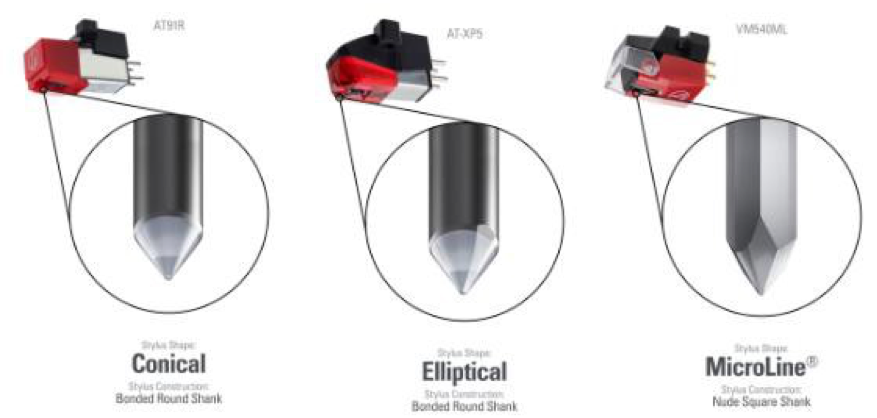

Conical- and elliptical-shaped styli are commonly used in commercial applications. The conical shape is recommended for heavy back-cueing and scratching, requirements typically found in commercial applications such as club or competition DJing. When intended specifically for this application, the “DJ cartridge” will also employ an enhanced suspension system designed to withstand the rigors of heavy use and abuse. The conical stylus is also suitable as an entry-level hi-fi stylus, offering a good performance-to-price ratio. Conical styli are durable, less fussy to align, can withstand higher tracking forces, and are low in cost due to the ease of manufacturing them.
The elliptical-shaped stylus may be used for light back-cueing and scratching, but is primarily designed to give professional DJs the best high-fidelity performance from their records. We use an elliptical-shape stylus on the AT-XP5 DJ Cartridge supplied with our AT-LP1240USB XP DJ Turntable. The longer side of the elliptical shape allows more contact with the groove wall, resulting in more detail to be extracted from the groove. Compared to the spherical stylus, the biradial stylus does a better job of tracking the inner grooves of a record. Distortion and record wear when tracking the inner grooves will be lower. The elliptical stylus offers improved sound and less wear at a slightly higher cost. The use of an alignment tool, such as a cartridge alignment protractor, is recommended when setting up a biradial stylus to obtain optimal performance.
The benefits of more detailed reproduction and lower tracking distortion also make the elliptical-shaped stylus a popular choice for listening at home, especially when used in conjunction with a better quality hi-fi system. These same benefits also make it a good choice for transferring records to a digital format where faithful transfer of the signal is paramount.
Hyper-elliptical styli can vary slightly in size, but just as importantly, their unique shapes provide added sonic benefits and lower contact pressure compared to less sophisticated styli. Lower noise and decreased record and stylus wear are major benefits of hyper-elliptical designs. Due to their complex shapes, the use of an alignment tool is highly recommended when setting up a hyper-elliptical styli.
If you have additional questions about styli or turntables, please contact the Audio Solutions Department for assistance.






























































































































.webp)