What are the differences between the microphones that Audio-Technica offers? (Part 3 – Condenser Mics)
Answer: The last two weeks our Question of the Week focused on the topic of types of microphones, and we covered both moving-coil dynamic and ribbon microphones. This week we’ll conclude with condenser microphones. Condenser microphones come in two forms: electret condenser and DC-biased condenser. The difference between the two is that the DC-biased condenser requires an external power supply to provide polarizing voltage while the electret condenser uses a pre-polarized diaphragm or back plate. Most condenser microphones used today are electret.
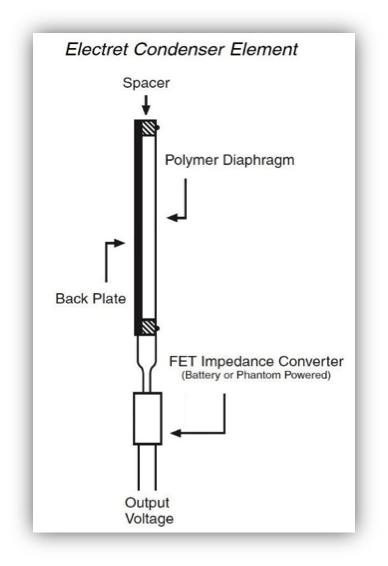 Both electret and DC-biased condenser microphones utilize a thin polymer diaphragm and a fixed back plate that act as opposite sides of a capacitor. Change in air pressure (sound) moves the diaphragm and changes the capacitance of the circuit, thus creating a change in electrical voltage. The low-mass diaphragms used in Audio-Technica condenser microphones allow for lower handling and mechanical noise. Condenser microphones are used in many recording and broadcast applications as they provide a natural, clean, clear, detailed, and transparent replication of the sound source. Condensers can also be much smaller than dynamic elements, making them the ideal choice for lavaliers and other miniature microphones. Audio-Technica has also pioneered an innovative honeycomb diaphragm design which allows for additional surface area to enhance the microphone’s performance. This new design is used in Audio-Technica microphones such as the AT2035 and the AT5040. You may view a variety of Audio-Technica condenser microphones in every one of our popular Basic Recording Techniques Videos.
Both electret and DC-biased condenser microphones utilize a thin polymer diaphragm and a fixed back plate that act as opposite sides of a capacitor. Change in air pressure (sound) moves the diaphragm and changes the capacitance of the circuit, thus creating a change in electrical voltage. The low-mass diaphragms used in Audio-Technica condenser microphones allow for lower handling and mechanical noise. Condenser microphones are used in many recording and broadcast applications as they provide a natural, clean, clear, detailed, and transparent replication of the sound source. Condensers can also be much smaller than dynamic elements, making them the ideal choice for lavaliers and other miniature microphones. Audio-Technica has also pioneered an innovative honeycomb diaphragm design which allows for additional surface area to enhance the microphone’s performance. This new design is used in Audio-Technica microphones such as the AT2035 and the AT5040. You may view a variety of Audio-Technica condenser microphones in every one of our popular Basic Recording Techniques Videos.
Condenser microphones’ internal FET impedance matching circuity requires additional power which the microphones get in different ways. Some mics utilize battery power, some bias power, but most use what is commonly referred to as “phantom power.” This power comes in the form of external DC voltage, often provided by the device the microphone is connected to. This may be an audio console, recording interface, or a device like the AT8801 Single Channel Phantom Power Supply. Additional in-depth information on phantom power can be found in our Question of the Week on power modules.
We hope you found this series on the different types of microphones to be helpful. Each type of microphone can be used for different applications, so don’t be afraid to simply use your ears to determine which mic sounds best to you. If, however, you’d like assistance in determining which Audio-Technica microphone might best suit your needs, please contact our Audio Solutions Department.
Check back next Thursday when we’ll tackle another Question of the Week.































































































































.webp)